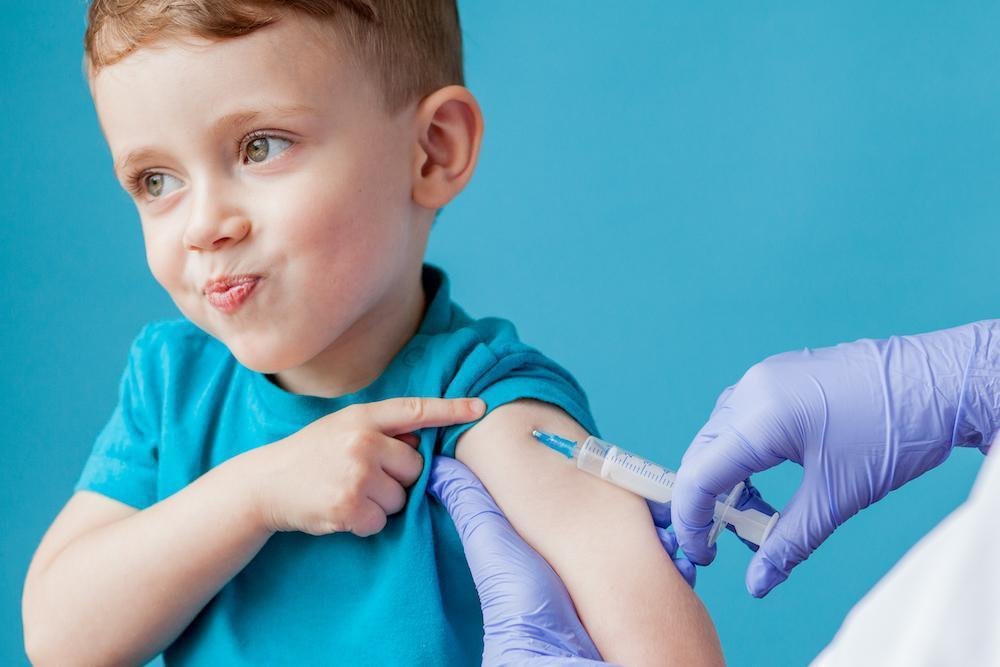
Immunizations are a critical aspect of maintaining public health and preventing the spread of contagious diseases. For children, these vaccines are not only crucial for their individual health but also play a significant role in protecting the wider community. Understanding the essential immunizations for children helps parents make informed decisions and ensure their child’s optimal health and safety.
Why Immunizations are Important
Immunizations are designed to protect children from diseases that can be serious, or even deadly. Vaccines work by stimulating the body’s immune system to recognize and fight off specific pathogens. This preparation helps children build immunity without having to suffer from the actual diseases. By getting vaccinated, children contribute to herd immunity, which helps protect those who cannot be vaccinated, such as infants, elderly individuals, or those with weakened immune systems.
Routine Vaccines for Infants and Toddlers
The early years of a child’s life are crucial for vaccinations. The routine immunizations recommended for infants and toddlers include:
- Hepatitis B Vaccine: Administered shortly after birth, this vaccine protects against hepatitis B, a virus that can cause serious liver infections and long-term liver damage.
- Diphtheria, Tetanus, and Pertussis (DTaP) Vaccine: This combination vaccine protects against three diseases. Diphtheria can cause severe respiratory issues, tetanus leads to painful muscle stiffness, and pertussis, also known as whooping cough, is a highly contagious respiratory illness.
- Haemophilus influenzae Type b (Hib) Vaccine: The Hib vaccine protects against bacterial infections that can lead to serious diseases such as meningitis and pneumonia.
- Polio Vaccine (IPV): This vaccine protects against polio, a virus that can cause paralysis and is highly infectious.
- Pneumococcal Vaccine (PCV13): It protects against pneumococcal diseases, including pneumonia, meningitis, and blood infections.
- Rotavirus Vaccine: Rotavirus causes severe diarrhea and vomiting, which can lead to dehydration. This vaccine helps prevent these complications.
- Measles, Mumps, and Rubella (MMR) Vaccine: This combination vaccine protects against three viral infections. Measles can cause serious complications like pneumonia and encephalitis, mumps can lead to swelling of the salivary glands, and rubella can result in birth defects if contracted during pregnancy.
- Varicella (Chickenpox) Vaccine: This vaccine protects against chickenpox, a highly contagious disease characterized by an itchy rash and fever.
Vaccines for Older Children
As children grow, they require additional vaccines to continue protecting them from various diseases. These include:
- Hepatitis A Vaccine: Hepatitis A is a liver infection spread through contaminated food and water. The vaccine is recommended for older children who did not receive it in infancy.
- Tetanus, Diphtheria, and Pertussis (Tdap) Booster: A booster dose is needed around age 11 or 12 to maintain protection against these diseases.
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Vaccine: Recommended for preteens, this vaccine protects against cancers caused by human papillomavirus, including cervical cancer and other cancers related to HPV.
- Meningococcal Vaccine: This vaccine protects against bacterial meningitis and septicemia, which can be severe and life-threatening.
- Seasonal Influenza (Flu) Vaccine: Annual flu vaccines are recommended to protect against the seasonal influenza virus, which can cause widespread illness.
Vaccination Schedule and Catch-Up Vaccines
Vaccines are administered according to a recommended schedule, which ensures that children receive their immunizations at the optimal times to build immunity. This schedule is regularly updated based on new research and changes in disease patterns. If a child misses any vaccines, catch-up schedules are available to help bring them up-to-date.
Safety and Side Effects
Vaccines undergo rigorous testing for safety and efficacy before they are approved for use. While side effects can occur, they are usually mild and temporary, such as a sore arm or a mild fever. Serious side effects are rare. Vaccines are continuously monitored for safety, and any potential risks are weighed against the benefits of preventing disease.
Addressing Concerns and Misconceptions
Some parents may have concerns or misconceptions about vaccines. Common myths, such as vaccines causing autism or containing harmful levels of toxins, have been thoroughly debunked by scientific research. It is important to rely on credible sources and consult healthcare professionals to address any concerns and make informed decisions about vaccination.
The Role of Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers play a crucial role in educating parents about the importance of vaccinations and ensuring that children receive their vaccines on time. They can provide up-to-date information, answer questions, and help navigate any concerns or special considerations.
Conclusion
Immunizations are a fundamental aspect of child health and public safety. By staying informed about the essential vaccines and adhering to the recommended schedule, parents can help protect their children from preventable diseases and contribute to the overall well-being of the community. Ensuring that children are fully vaccinated is a simple yet powerful way to promote their health and safety.