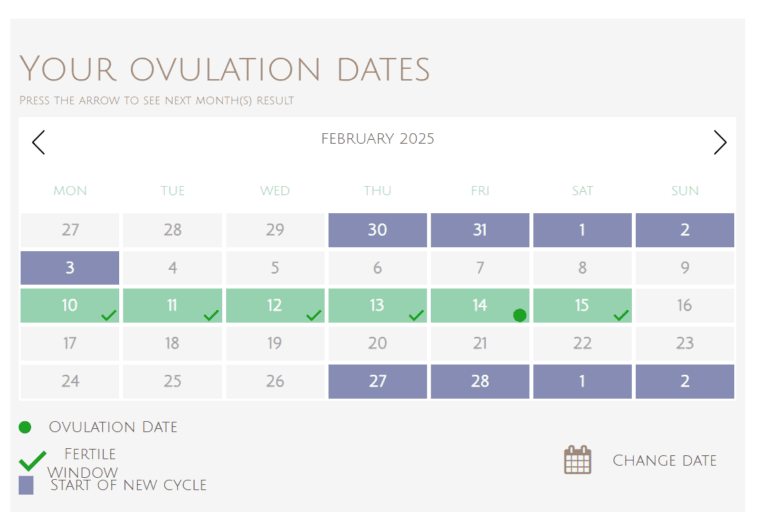
Tracking ovulation is one of the most effective ways to boost your chances of conception. An ovulation calculator helps you predict your most fertile days by estimating when you’re likely to ovulate based on your menstrual cycle. Whether you’re trying to conceive or simply want to understand your reproductive health better, using an ovulation calculator can provide valuable insights. In this guide, we’ll explain how ovulation calculators work, how to use them, and why tracking your cycle can make a difference on your fertility journey.
[ovulationcalculator]
If you experience irregular periods or simply want to learn more about calculating ovulation, there are various methods to help you identify your most fertile days.
How to Calculate Ovulation
Understanding how to calculate ovulation is a crucial aspect for individuals seeking to enhance their knowledge of their menstrual cycle. Ovulation typically occurs around the midpoint of the menstrual cycle, marking a key period for conception. There are several effective methods to determine the ovulation date, two popular approaches being the calendar method and the luteal phase method.
The calendar method involves tracking the menstrual cycle for several months to identify a pattern. Most women have a cycle ranging from 21 to 35 days. Once the length of the cycle is determined, ovulation can be estimated by counting 14 days before the start of the next period. For instance, if an individual’s cycle averages 30 days, ovulation would likely occur around day 16. Keeping a calendar or using a cycle tracking app can greatly assist in this process, making it easier to visualize and predict ovulation timing.
Alternatively, the luteal phase method focuses specifically on the period after ovulation. This phase lasts about 14 days, which is consistent for most women regardless of cycle length. By observing the start of the next menstrual cycle, one can count backwards to estimate when ovulation took place. For example, if the next period starts on day 28, ovulation likely occurred around day 14. By combining these methods, individuals can gain a more accurate understanding of their ovulation window.
In addition to these methods, being mindful of physical signs such as changes in cervical mucus or basal body temperature can further aid in determining ovulation. Consistent cycle tracking not only enhances one’s ability to predict ovulation but also fosters a deeper connection with one’s body, paving the way for informed reproductive health decisions.
Utilizing Ovulation Kits
Ovulation kits serve as valuable tools for individuals seeking to track their menstrual cycle and identify their peak fertility days. These kits come in various forms, including urine-based tests and digital monitors, each designed to detect the luteinizing hormone (LH) surge, which typically precedes ovulation by 12 to 36 hours. Urine-based kits, most commonly found in pharmacies, usually involve dipping a test strip into urine or urinating directly onto the strip. Digital monitors, on the other hand, analyze hormonal changes and provide more advanced insights, often tracking multiple hormonal indicators to offer a more comprehensive view of the menstrual cycle.
Understanding when to use these kits is crucial for accurate results. It is advisable to begin testing several days before ovulation is expected, which typically occurs midway through the menstrual cycle. For individuals with regular cycles, ovulation usually occurs approximately 14 days before the onset of menstruation. Therefore, tracking cycles consistently can help in predicting the ideal window for testing. However, irregular cycles may necessitate a different approach, potentially involving consultation with a healthcare provider for best practices.
Interpreting the results involves careful observation of the test lines or digital readouts. A positive result is indicated by the test line being as dark or darker than the control line, signaling that ovulation is imminent. It is essential to remember that this peak fertility period is considered the day of the LH surge and the following day, making timely intercourse during this window critical for those trying to conceive. Proper utilization of ovulation kits, alongside consistent menstrual tracking, can empower individuals to better understand their reproductive health and optimize their chances of conception.
Recognizing Signs of Ovulation
Understanding the signs of ovulation is an essential aspect of mastering the menstrual cycle. Ovulation, the process in which a mature egg is released from the ovary, typically occurs mid-cycle. Several physical and hormonal indicators can help individuals recognize this significant time in their cycle. One of the most prominent signs is changes in cervical mucus. As ovulation approaches, the cervix produces more slippery, clear, and elastic mucus, resembling egg whites. This consistency aids sperm mobility, thus increasing the chances of conception. Tracking these variations can offer valuable insight into one’s fertile window.
Another sign to monitor is basal body temperature (BBT). Before ovulation, a person’s BBT is generally lower, but it experiences a subtle rise (typically 0.5 to 1 degree Fahrenheit) after ovulation due to increased progesterone levels. By charting daily BBT, individuals may identify a distinct pattern, allowing them to pinpoint when ovulation has occurred. This method not only helps predict ovulation but can also assist in understanding overall menstrual cycle patterns.
Ovulation pain, also known as Mittelschmerz, is another indicator that some individuals experience. This localized pain, often felt on one side of the lower abdomen, can occur just before or during the release of an egg. While the intensity varies among individuals, it serves as a compelling reminder of the ovulation phase. Additionally, some may notice breast tenderness or sensitivity during this time, a secondary effect of hormonal fluctuations. Recognizing these signs of ovulation, such as changes in cervical mucus, BBT shifts, and physical discomfort, equips individuals with the knowledge needed to embrace their fertility journey effectively.
Tracking Basal Body Temperature (BBT)
Basal body temperature (BBT) is the lowest recorded body temperature during rest, usually measured after a period of sleep. Tracking BBT can be an effective method for identifying ovulation, as subtle temperature shifts can indicate hormonal changes associated with the menstrual cycle. Typically, a woman’s BBT remains relatively low until ovulation, when it experiences a slight increase, usually around 0.5 to 1 degree Fahrenheit. This rise is predominantly due to the hormone progesterone, which is released after an egg is released from the ovary.
To accurately measure BBT, it is crucial to use a basal thermometer, which provides precise readings to the tenth of a degree. For the most reliable results, measurements should be taken each morning at the same time, before getting out of bed or engaging in any physical activity. It is also advisable to ensure that the individual has at least three hours of continuous sleep before taking the measurement. This consistency helps establish a clearer temperature pattern over time.
Once measurements are taken, they can be plotted on a chart to observe the changes in BBT throughout the menstrual cycle. Typically, a distinct temperature rise of more than 0.2 degrees Fahrenheit sustained for at least three days is a strong indication that ovulation has occurred. This data can be invaluable, particularly for those trying to conceive, as it allows for better timing of intercourse during the fertile window. By regularly tracking BBT, women can gain deeper insights into their cycle, anticipate ovulation, and make informed decisions regarding their reproductive health.
Combining Methods for Accuracy
When it comes to mastering ovulation and understanding one’s menstrual cycle, employing a combination of tracking methods can lead to more reliable results. Each method offers unique insights, and when utilized together, they can paint a comprehensive picture of reproductive health. The primary techniques include calendar tracking, ovulation prediction kits (OPKs), and basal body temperature (BBT) charting.
Calendar tracking involves marking menstrual cycles on a calendar to predict ovulation based on the average cycle length. While this method is beneficial, it relies heavily on regularity. Irregular cycles can lead to inaccurate predictions. By incorporating ovulation kits, which detect the surge in luteinizing hormone (LH) that occurs just before ovulation, individuals can gain a clearer indication of their most fertile days. OPKs are especially useful for those who may not have consistent cycles, as they provide real-time data to confirm ovulation.
Basal body temperature monitoring adds another layer of accuracy. This method involves taking the temperature first thing in the morning before any activity, noting slight increases that indicate ovulation has occurred. While BBT alone is retrospective, meaning it confirms ovulation after it has already occurred, it can be extremely beneficial when combined with the other methods. By correlating calendar data, ovulation kit results, and temperature fluctuations, individuals can effectively enhance their understanding of their menstrual cycle.
Furthermore, recording each of these data points within a dedicated app or journal can facilitate better tracking over time. This allows for the identification of patterns and trends, leading to even more precise predictions in future cycles. Ultimately, integrating multiple ovulation tracking methods provides a holistic approach, contributing to improved accuracy and a deeper understanding of one’s reproductive health.
Common Obstacles in Ovulation Tracking
Tracking ovulation can be a valuable tool for individuals seeking to understand their menstrual cycles and optimize their reproductive health. However, several common obstacles can hinder the accuracy and effectiveness of ovulation tracking. One prevalent challenge is the occurrence of irregular menstrual cycles. Many individuals experience cycles that vary in length, making it difficult to accurately predict ovulation. This inconsistency can stem from various factors, including stress, lifestyle changes, or underlying health conditions.
Another significant factor affecting ovulation tracking is hormonal imbalances. Hormones such as estrogen and progesterone play critical roles in regulating the menstrual cycle. Any disruption in their levels can lead to changes in cycle regularity and ovulation timing. Conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or thyroid disorders can further complicate the tracking process, resulting in missed ovulation windows and uncertainty regarding fertility.
Moreover, external factors can also influence ovulation. Stress, inadequate sleep, changes in diet, and intense physical exercise can all impact hormonal balance and, consequently, ovulation. This complex interplay between internal and external factors can create inconsistencies in tracking efforts. Fortunately, several strategies can help mitigate these obstacles. Keeping a detailed menstrual diary can provide insights into personal cycle patterns, enabling individuals to anticipate ovulation more accurately even in the presence of irregular cycles.
Integrating ovulation predictor kits (OPKs) into one’s routine can also enhance tracking accuracy, as they measure hormone levels in urine to identify peak fertility. Additionally, maintaining a healthy lifestyle through balanced nutrition, regular exercise, and stress management techniques can support hormonal regulation and promote more regular cycles. By acknowledging and addressing these common obstacles, individuals can improve their ovulation tracking efforts and enhance their reproductive health.
Consulting with Healthcare Professionals
Monitoring ovulation and understanding one’s menstrual cycle can be crucial for those trying to conceive or manage reproductive health. Engaging with healthcare professionals can significantly enhance this journey. Consulting a qualified physician or a reproductive endocrinologist can provide insights tailored to individual needs, thereby facilitating a more effective approach to ovulation tracking.
It is advisable to seek professional guidance when discrepancies in the menstrual cycle occur, such as irregular cycles, missed periods, or any symptoms that suggest hormonal imbalances. These health concerns may indicate underlying conditions. For instance, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common endocrine disorder that affects ovulation and may require a specific treatment plan. By addressing such issues with a healthcare provider, individuals can receive appropriate interventions to improve ovulatory function and overall reproductive health.
Additionally, fertility specialists play a pivotal role for those who have been attempting to conceive without success. These professionals can offer advanced testing and tailored treatment options that may include hormonal therapies, lifestyle recommendations, and assisted reproductive technologies. Early consultation is beneficial; addressing fertility matters promptly can lead to more favorable outcomes.
Beyond fertility concerns, healthcare professionals can also assist in managing lifestyle factors that may affect ovulation. Nutrition, exercise, and stress management are vital components that can influence hormonal balance and menstrual regularity. By collaborating with healthcare experts, individuals can gain access to resources that align with their health goals while promoting overall well-being.
In summary, consulting with healthcare professionals regarding ovulation tracking and reproductive health is essential. Their expertise can guide individuals in managing underlying conditions and navigating fertility challenges, leading to informed decisions and improved reproductive outcomes.